Class 2: Reproducibility crisis
Methodology of Scientific Research
Andrés Aravena, PhD
February 25, 2022
62.3% of the world population has received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine
Today, according to “Our World in Data”
In other words, more than 37% of people has not been vaccinated
Why?
There are many reasons
Only 11.4% of people in low-income countries have been vaccinated
In rich countries we observe vaccine hesitance
Why people do not want to be vaccinated?
Again, there are many reasons
Political
Belief
Distrust of Science
Some people distrust Science
Besides the Anti-vaccine people, we have
Climate change denial
Flat Earthers
and several others
Can Science be trusted?
PLOS Medicine 2005

Most Scientists are honest
In 2009, 2% of scientists admitted to falsifying studies at least once
14% admitted to personally knowing someone who did
Most people do not lie
Replicability crisis
A 2016 poll of 1,500 scientists reported that 70% of them had failed to reproduce at least one other scientist’s experiment
50% had failed to reproduce one of their own experiments
There are problems with the experiments and their analysis
Science August 2015•vol 349 issue 62519
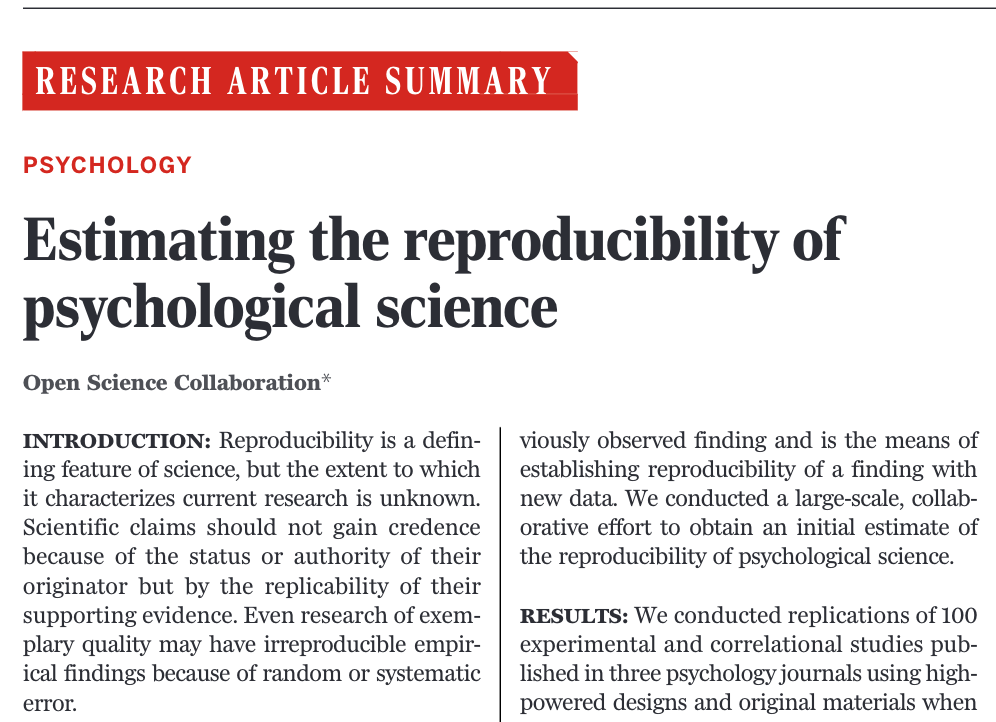
Summary
Repeated the top 100 studies in psychology
- Only 36% of the replications gave significant findings
- compared to 97% of the original studies
- The effect size in the replications was half of the effect size in the original studies, on average
This is not limited to psychology
Why does this happens?
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society and American Statistical Association

Cargo cults

This has been said before

Richard Feynman
- Physicist
- Excellent professor
- Worked in the Manhattan Project at 25 years old
- Nobel Prize on Physics in 1965
- He was talking about USA in the 1970s
Cargo-cult statistics
“the ritualistic miming of statistics rather than conscientious practice”
Cargo-cult statistics and scientific crisis
“practitioners go through the motions of fitting models, computing p-values or confidence intervals, or simulating posterior distributions”
“They invoke statistical terms and procedures as incantations, with scant understanding of the assumptions or relevance of the calculations, or even the meaning of the terminology”
The authors say
“We believe that poor statistical education and practice are symptoms of and contributors to problems in science as a whole”
My opinion
As someone who teaches maths and statistics, I say
We are bad at teaching maths
We need to find better ways to teach math
(in particular to math teachers)
Math is a superpower
Math allow us to travel in time, and see the invisible
That is why people who knows do not want to teach math:
It gives power to the people
“They” do not want you to know math
Quick test
Setup
We do an experiment E
We get some data X
We define null and alternative hypotheses H0, H1
We do an hypothesis test
What is a p-value?
The probability that the null hypothesis is true, given that we observed X
The probability of observing X, assuming that the null hypothesis is true
The answer is
2. The probability of observing X, assuming that the null hypothesis is true
But many people believe it means the first option
P-values do not mean what many people thinks
The order matters
Probabilities depend on two things
- The event we are evaluating A
- What we know about the state of the system B
We say “probability of A given B”
They are not interchangeable
Example: diagnosis
Imagine that you are randomly chosen for a test of COVID-19
The result is “positive”. It says that you have the virus
But this test fails 2% of times, giving a false positive or a false negative
Then the question:
What is the probability that you have COVID-19 given that the test said “positive”?
It is not 98%
The test is correct 98% of times
That is, the probability of a positive test given that you have COVID
But we really want to know the probability of COVID given that the test is positive
They are not the same
We need to know the base rate
To answer this question we must know the prevalence of COVID
That is, what is the proportion of the population with COVID
There are 728,692 active cases in Turkey today
(only 1,128 are serious)
Population of Turkey is 85,828,516
Dividing both numbers we find that the prevalence is 0.86%
Let’s fill this matrix
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | . | . | . |
| COVID+ | . | . | . |
| Total | . | . | . |
COVID reality in the rows and test results in the columns
Let’s assume that there is a million people
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | . | . | . |
| COVID+ | . | . | . |
| Total | . | . | 1000000 |
We will fill this matrix in the following slides
Assuming one million people makes the math easier
0.86% of them are COVID positive
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | . | . | 991400 |
| COVID+ | . | . | 8600 |
| Total | . | . | 1000000 |
Prevalence is the percentage of the population that has COVID.
In other words, it is the probability of (COVID+)
98% are correctly diagnosed
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | 971572 | . | 991400 |
| COVID+ | . | 8428 | 8600 |
| Total | . | . | 1000000 |
Precision is the probability of a correct diagnostic
(Here we assumed that the error rates are the same for positive and negative. That may not be the case always)
2% are wrongly diagnosed
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | 971572 | 19828 | 991400 |
| COVID+ | 172 | 8428 | 8600 |
| Total | . | . | 1000000 |
(this error rate is only an example. Real tests are usually better)
Total people diagnosed
| Test- | Test+ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID- | 971572 | 19828 | 991400 |
| COVID+ | 172 | 8428 | 8600 |
| Total | 971744 | 28256 | 1000000 |
We sum and fill the empty boxes
28256 people got positive test, but only 8428 of them have COVID
Probability of having COVID if the text is positive: 29.83%
Recommended book

Another recommendation
The same book with two names, for different markets


Shall we learn Math?
There are several reasons to learn math
- Utilitarian
- To pay the bills and not be cheated
- To get the proper concentrations in the lab
- Practical
- To design the experiments
- To analyze the results of the experiment
- Philosophical
- Understand the meaning of the results
- Connect experiments with the rest of human knowledge
Galileo said
The universe […] cannot be understood unless one first learns […] the language and interpret the characters in which it is written. It is written in the language of mathematics, […] without these, one is wandering around in a dark labyrinth.
Galileo Galilei (1564 – 1642),
Italian astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and
mathematician
Maths and Biology
Mendel discovered genes using only math
Galton created the first Department of Genetics, and linear correlation
Fisher invented statistics while working at Agricultural research
“Student’s test” was invented by biotech working in beer
Math is cultural patrimony of humanity
It has been invented and developed independently in several places:
- ancient Babylon, ancient Egypt,
- ancient Greece (all around Mediterranean and Aegean sea),
- China, India,
- Pre-hispanic Mexico, Golden Age Persia,
- European Renaissance, Industrial England, Soviet Union, etc.
We have mathematicians in Turkish money.
Math is cultural patrimony of humanity
- We need to learn math to receive this cultural legacy
- We speak about “Universal literature”
- Architecture
- Painting and Sculptures
- Music
- Cinema
Mathematic belongs to all humanity
Research when you do not know math
It is like moving in the city using only the metro:
easy, but you can only go to places that others have already prepared
These places are crowded, and it is hard to be noticed here.
Research when you know some math
It is like having your own car. Depending on your knowledge level, it can be
- a taxi (someone else drives),
- an sedan car (you drive on paved streets),
- a jeep (you can go to much more places, you can fix up when things break down), or
- an experimental autonomous car (you design a new car from the zero)
What do you need to know
You need at least to understand enough mechanics to know
- when to put gasoline,
- When to change oil,
- maybe how to change a tire,
- How to talk to the mechanic so he does not cheat you.
Math is a tool for thinking
To have correct answers we must ask the correct questions
This is the real reason we need math
Mathematics is not about numbers, equations, computations or algorithms: it’s about understanding
William Paul Thurston (1946 – 2012),
American mathematician
Abstraction
According to “Understanding Comics”

According to “Understanding Comics”


Abstraction means “generalization”
It is easier to solve a problem when we discard irrelevant details
Abstract problems can correspond to several applied problems
Solving one solves all of them
These connections help us to understand new problems by analogy to old ones
Doing math is like running 🏃🏻
- It requires energy and willpower
- Everybody can run 10K … if trained correctly

Who do you want to be?


References
Erika Check Hayden, Weak statistical standards implicated in scientific irreproducibility Nature, 11 November 2013
Open Science Collaboration, Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science 28 Aug 2015: Vol. 349, Issue 6251, aac4716
Replications can cause distorted belief in scientific progress Behavioral and Brain Sciences, Volume 41, 2018, e122 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X18000584. Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 July 2018
More References
Reproducibility of Scientific Results Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
T.D. Stanley, Evan C. Carter and Hristos Doucouliagos What Meta-Analyses Reveal about the Replicability of Psychological Research Deakin Laboratory for the Meta-Analysis of Research, Working Paper, November 2017
Silas Boye Nissen, Tali Magidson, Kevin Gross Is a corresponding author, Carl T Bergstrom Research: Publication bias and the canonization of false facts eLife Dec 20, 2016; 5:e21451
