September 27th, 2018
How this course works
The Goal
The purpose of this course is to learn to think with data
Not to study
Not to teach
But to learn
What is learning?
To learn is to change our behavior rules
We think different, we act different
We think with two strategies:
- analytical
- automatic
So learning has to be in two stages
How do we learn?
We learn what we do, not what we study
Like riding a bike
Can you learn to dance only reading Wikipedia?
Some theory, a lot of practice
Failure is expected. We learn from failure. Try judo
Why learning is hard?
Not always. Kids learn easily.
We have difficult learning new things because we have to unlearn old habits.
So we will need to make an extra effort
Cognitive styles
how people remembers
According to cognitive research, there are three main ways of remembering
- A few people remembers what they see
- Some people remembers what they listen
- Most people remembers what they do
- Kinesthetic sense: body position
- “The pen is mightier than the keyboard”
Moreover logic is tightly connected with language
Note taking
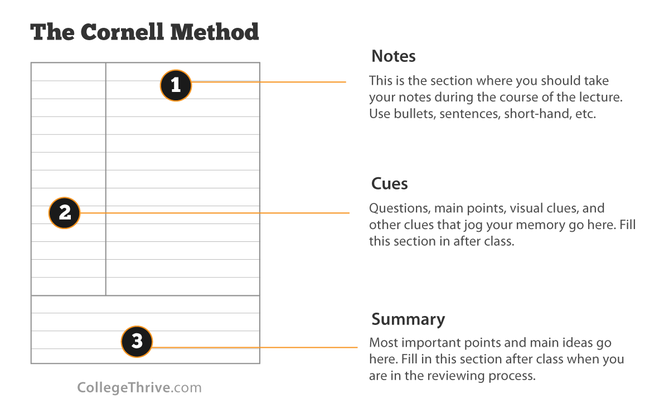
Search in Google or YouTube: Cornell Method
Focusing
It’s easy to get distracted,
specially when we don’t like the task
We learn by getting out of or “comfort zone”
Learning is uncomfortable, even annoying
We have to push ourselves to focus
Pomodoro technique
- set a timer for 25 minutes
- force yourself to focus on that period
- no email, no Facebook, no toilet, no coffee/cigarettes
- in case of interruption, restart from zero
- when the bell rings STOP working for 5 minutes
- every 3 Pomodoros, take a 20 min break
We will use this technique in this course 
How memory works
We have roughly three stages of memory
- very short term memory (seconds)
- medium term memory (hours)
- long term memory (years)
Transition between medium and long term memory happens when we sleep (and dream)
That is why we have 2 sessions per week
Learning strategy
my proposal
Attend to classes regularly (always!)
Bring a notebook and a pen
Handwrite what we speak, and your own questions
Summarize at the end of the class (Cornell Method)
Speak with your classmates
Sleep well (but not during the class)
Easy is bad
For every complex problem there is always a simple, direct and wrong solution
We may want an easy way, but that is a bad idea
- We learn better when there is some desired difficulty
- If it is easy, a robot can do it
- Nobody is proud of doing something easy
Kolay Gelsin
Course Forum
Ask your questions (and give your answers) on the forum
See how to register at anaraven.bitbucket.io/blog/2018/icsp/
Everybody must fill the online survey to get access to the course forum
Be honest
Bits and Bytes
Memory is measured in Bytes
Remember: one byte = one letter
Computer Science people thinks in Bytes
A number between 0 and 255
That is, 256 combinations. Why?
Communication is measured in bits
 Telecommunication engineers think in bits
Telecommunication engineers think in bits
One bit = “on” or “off”
Easy to detect with electronics
Can represent: true/false, yes/no, high/low, in/out, up/down, left/right, north/south, east/west, male/female, 1/0
Young or Old?
Your undergrad study is 4 years, which we can split in two groups: Old and Young
We can represent each group with 1 and 0
In each group we can split again in two: Begin and End
We can also represent them with 1 and 0
The we have two semesters: Spring and Fall
Combinations
| O/Y | B/E | S/F | Bits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Old | End | Spring | 111 |
| Old | End | Fall | 110 |
| Old | Begin | Spring | 101 |
| Old | Begin | Fall | 100 |
| Young | End | Spring | 011 |
| Young | End | Fall | 010 |
| Young | Begin | Spring | 001 |
| Young | Begin | Fall | 000 |
One more bit = double combinations
Each time we split in half, we multiply by two the combinations’ number
| Num Bits | Num Combinations | Num Bits | Num Combinations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 32 |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 64 |
| 3 | 8 | 7 | 128 |
| 4 | 16 | 8 | 256 |
Powers of 2
This is the reason why we use powers of 2
Learn these:
| Num Bits | Num Combinations | Num Bits | Num Combinations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 16 | 10 | 1024 |
| 8 | 256 | 20 | 1048576 |
| 16 | 65536 | 32 | 4294967296 |
Kilos versus kilos
In Science we use the decimal system
1 kilo = 1000 units
In Computing this is usually replaced by 210=1024
1 Kilo = 1024 units
Similar but not the same
Take care of Megas and Gigas
The difference between kilo and Kilo is 2.4%
The difference for Mega is 4.8%
The difference for Giga is 7.3%
Be careful when you buy a hard disk
Decimal to bits
2018 / 2 = 1009, reminder 0
1009 / 2 = 504, reminder 1
504 / 2 = 252, reminder 0
252 / 2 = 126, reminder 0
126 / 2 = 63, reminder 0
63 / 2 = 31, reminder 1
31 / 2 = 15, reminder 1
15 / 2 = 7, reminder 1
7 / 2 = 3, reminder 1
3 / 2 = 1, reminder 1
1 / 2 = 0, reminder 1
11111100010
How to write less
Binary is practical but hard to write
First, we separate in groups of four
0111 1110 0010
Then we replace every group of four by a number or letter
Hexadecimal
| Binary | Hex | Binary | Hex |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 0 | 1000 | 8 |
| 0001 | 1 | 1001 | 9 |
| 0010 | 2 | 1010 | A |
| 0011 | 3 | 1011 | B |
| 0100 | 4 | 1100 | C |
| 0101 | 5 | 1101 | D |
| 0110 | 6 | 1110 | E |
| 0111 | 7 | 1111 | F |
Example
Sometimes Web address use HEX symbols