- Assistant Professor at Molecular Biology and Genomics Department
- Mathematical Engineer, U. of Chile
- PhD Informatics, U Rennes 1, France
- PhD Mathematical Modeling, U. of Chile
- not a Biologist
- but an Applied Mathematician who can speak “biologist language”
September 19th, 2018
I am Andres Aravena
I come from Chile
world
Chile
chile
Small country of 17 million people
Spanish colony 500 years ago (so language is Spanish)
Independent Republic 200 years ago
First Latin American country to recognize Turkish republic
Everyday life very similar to Turkey
Chileans like Turkish soap operas

binbirgece
Latin America in Turkey
Foreigners enrich the hosting countries. Just look at the food:
- Corn is from North and South America: maiz
- Tomato is Mexican: tomates
- Potato is from Chile and Peru: patatas
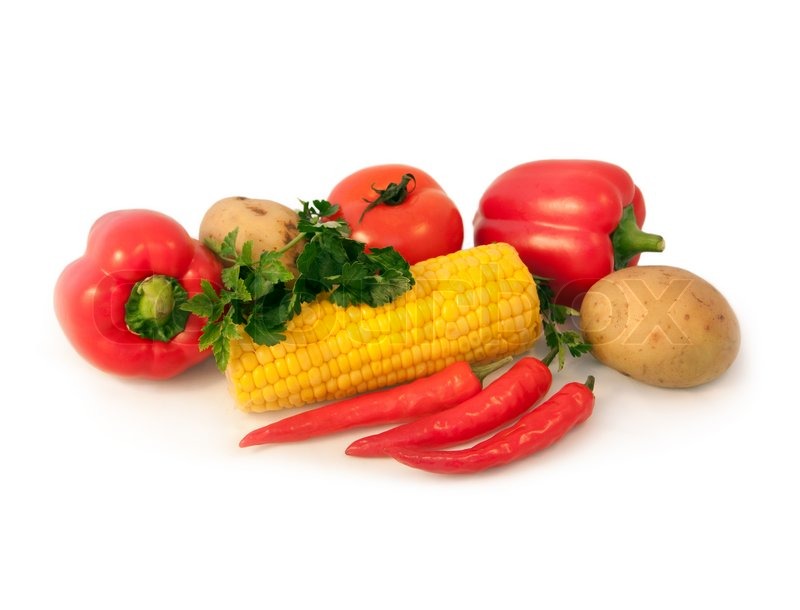

Diversity increases opportunities
Why computers?
for Science and beyond
Computers are rule changers
Modern computers were created to solve math equations
Then they were used to handle big databases
They became cheap and found everywhere
They became communication tools
They transformed society and science
How many computers do you use?
- Cellphone
- TV
- Cable decoder
- Microwave oven
- Washing machine
- Car motor
- Metro
- Elevator
- Notebook
Computers transformed
- The banking industry
- The air travel industry
- The manufacturing
- The cars
- The movies
- Science
Four Paradigms of Science
according to Microsoft
1 Empiric
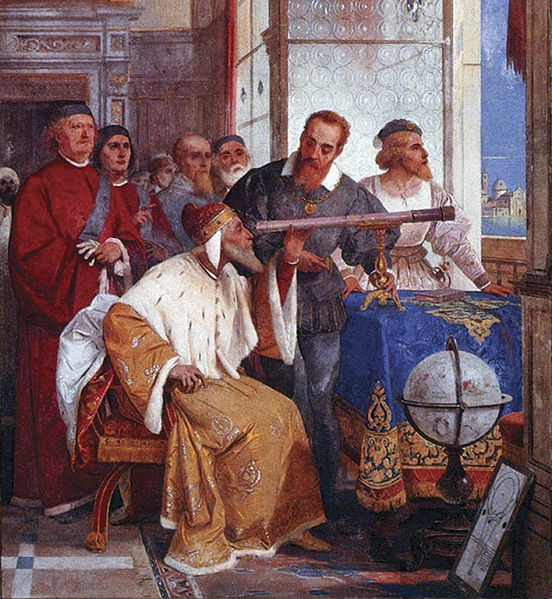

- observation of isolated facts
- description of related facts
- e.g. Botany, naming stars, Arab astronomers, Galileo, Tycho Brahe, Carl Linneaus
2 Theoretical
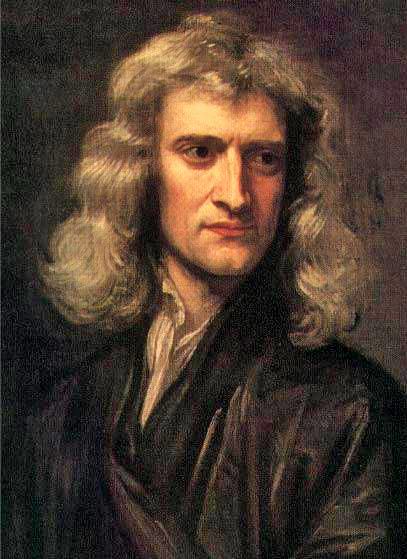

- Abstract models and theories
- Usually expressed in mathematical formulas
- Correct predictions validate the models
- e.g. Mendel laws of inheritance, Darwin natural selection theory, Kepler law of planet’s motion, Newton’s law of Gravity
3 Simulation Based
- Models that cannot be expressed in formulas
- Formulas that cannot be solved
- e.g. Protein structure prediction, three body problem, galaxy modeling
- Computational Astronomy, Computational Biology
John Von Neumann
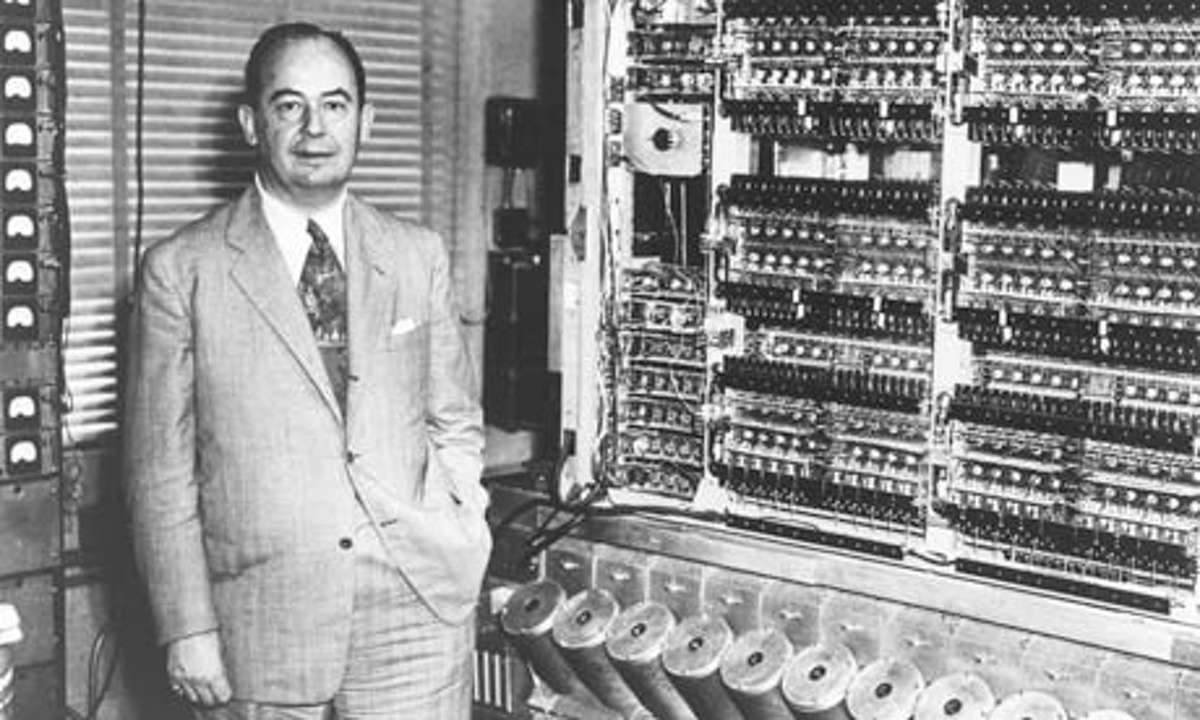
4 Data Based

- Discovering patterns hidden in data
- Huge volumes of data
- Complex interactions
- e.g. Bioinformatics, Astroinformatics, Data mining
Computers
Short history
- 1940’s
- First electronic computers. Used in the 2nd World War. Solving models for Manhattan project
- 1950’s
- Big computers sold to Governments for census, taxes
- Programs written manually by experts
- 1960’s
- Big computers in Banks and Airlines. Room size
- Mini-computers in research institutes. Wardrobe size
- First high level programming languages
More history
- 1970’s
- UNIX system made all mini-computers compatible
- first micro-computers at home. Desktop
- Internet at the US military
- 1980’s
- IBM made the first Personal Computer
- Microsoft created D.O.S. for personal computers
- Apple Macintosh, first home computer with windows and mouse
- Internet on Universities
- 1990’s
- Internet at home
- UNIX on personal computers