December 5, 2016
History of Science
Who is him?
Galileo Galilei
1564 – Born in Pisa, Italy
1581 – Enrols as medical student at U. Pisa
1589 – Appointed to Mathematics Chair, U. Pisa
1590 – Writes De Motu (On Motion), which is never published
1592 – Appointed professor of mathe at U. Padua, remains 18 years
1609 – Improves telescopes based on invention by Hans Lippershey
1610 – Publishes Sidereus Nuncius (Starry Messenger); views moon’s mountains and craters and 4 of Jupiter’s moons
1612 – Proposed Jupiter’s moons could be used as a universal clock for possible determination of longitude
On Motion
Galileo finds that moving objects follow mathematic equations > “The laws of Nature are written in the language of mathematics”
Describe relative motion:
- The speed of an object depends on the speed of the observer
- For example, if you are in a highway
- Cars in the same direction and speed seem to be on rest
- Cars in opposite directions have much higher speed
Relative motion laws
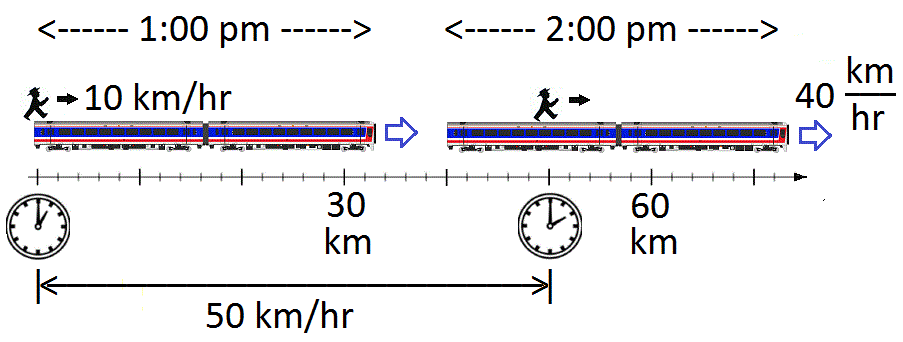
\[V_\text{Earth,Person}=V_\text{Earth,Train}+V_{\text{Train, Person}}\]
Tried to measure the speed of light
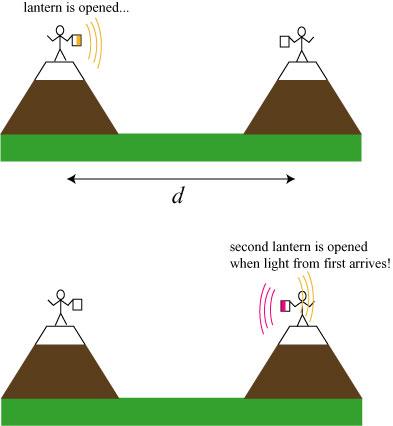
“It’s fast”
Discovers the moons of Jupiter

This helps other scientists
- At the same time that Galileo made his telescope, Kepler made a theory of the movement of planets
- “Kepler’s Laws”
- Isaac Newton completed it
- Invented Calculus
- Defined “Newton’s Laws of movement”
- Demonstrated that gravity laws explained Kepler’s Law
- People could make predictions of movements of planets
First measure of speed of light
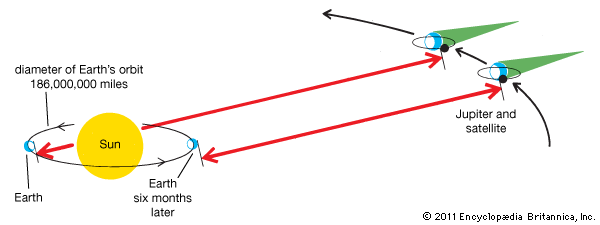
1676 by Danish astronomer Ole Rømer
“Luminiferous aether”
At that time the theory was that empty space was filled with a background medium called the luminiferous aether.
In that model light was a made of waves in aether
like waves in the water
The question was then
What is the speed of earth respect to aether?
Michelson & Morley experiment
In 1887, in Ohio, USA, Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley measured the speed of light in perpendicular directions
They tried to to detect the relative motion of the Earth through the stationary luminiferous aether
The data of this experiment is in the variable morley
Homework
Analyze morley data
- What type of data
- What do they mean?
- What is the conclusion?
- Why this is important in modern times?
- Hint: it is very important